To understand measurement and control it is worthwhile to reflect on the subject
of complete production control. This is especially important if one starts to look
at data-
By definition control means a continuous sequence of measuring, comparing to a set-
(While analysing the control loops, it is important to remember that some of them involve humans. Fully automatic production control hardly exists !)
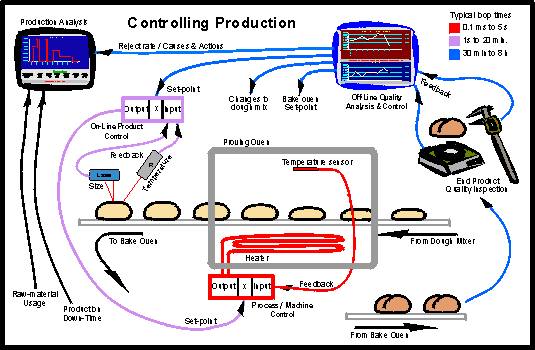
Process / Machine Control Loop -
This is the least complex and controls the operation of the production machinery.
It has a fast response to a change of the actual value because the feed-
On-
Like Quality Control this loop controls aspects of the end-
Off-
Often considered a burden, it is the most important process for letting you know what happens out on the factory floor. It is a slow loop because it involves measurement of all critical parameters of the end product and usually cannot be performed for 100 % of the production. It is therefore done in intervals from 30 minutes to 8 hours depending on the stability of the process.
In its most basic form it will allow you to make corrections to the set-
However, given the right tools, it can tell you when things start to go adrift before you start producing scrap, despite its relatively slow speed. This is because measuring all critical aspects allows you to see correlations between the movement of one parameter against another. Using statistical analysis allows you to pick a trend or identify machine problems before it's too late and any tolerances are exceeded.
The purpose of Quality Control is not to satisfy your customer but to PRODUCE THE BEST QUALITY PRODUCT WITH THE HIGHEST EFFICENCY. Obviously this also means doing your QC as efficiently and effectively as possible and using the data it produces for the analysis of your processes.
